
BEng in Microelectronics and Integrated Circuits
Degree Awarded: BEng in Microelectronics and Integrated Circuits
JUPAS Code: JS5250 (through admission to the Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering)
Abbreviated Title: BEng (MEIC)
Program Duration: Normally 4 years
Programme Outcomes(PO)
| PO1 | An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, microelectronics, and integrated circuits. |
| PO2 | An ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data. |
| PO3 | An ability to design efficient and economical microelectronics systems and integrated circuits, components, or processes subject to practical constraints. |
| PO4 | An ability to function in a multi-disciplinary environment through teamwork. |
| PO5 | An ability to identify, formulate and solve microelectronics and integrated circuits problems. |
| PO6 | An ability to understand professional practices and ethical responsibilities. |
| PO7 | An ability to communicate effectively. |
| PO8 | An ability to understand contemporary global, regional, economic, environmental, and social issues, and the corresponding role and the impact of microelectronics and integrated circuits design engineers. |
| PO9 | An ability to recognize the need for, and to engage in life-long learning. |
| PO10 | An ability to use current techniques, skills, and engineering tools necessary for solving microelectronics and integrated circuits problems. |
| PO11 | An ability to use the computer/IT tools relevant to microelectronics systems and integrated circuits design along with an understanding of their processes and limitations. |
The Curriculum
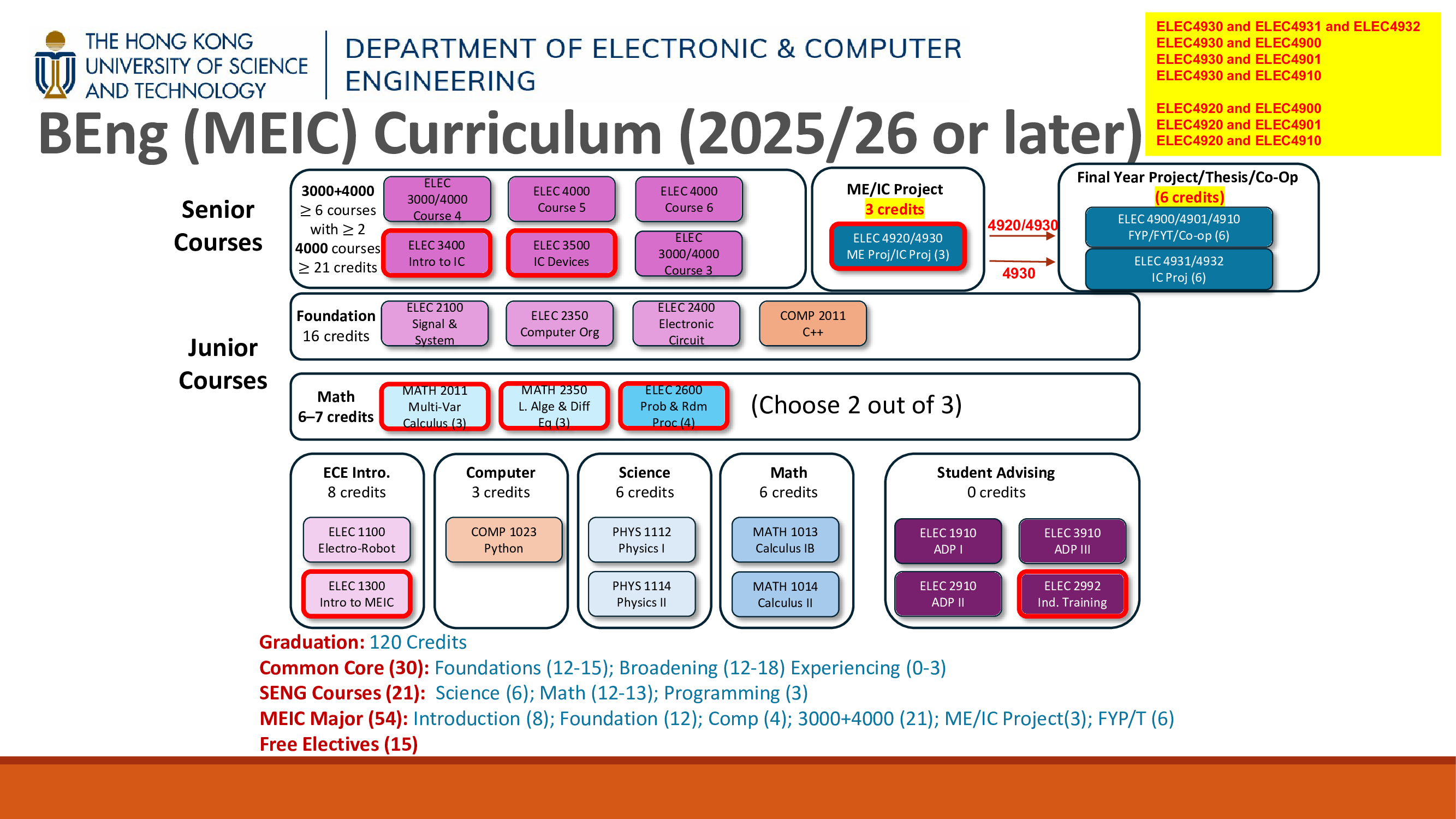

Research Option
Students may opt to graduate with or without an option. Students who take the Research Option must complete all requirements specified in addition to the major requirements.
Prerequisite
Students may refer to the latest course catalog to review the prerequisite requirements of the senior courses of interest and plan their course selection accordingly.
Critical Milestones
Students should follow critical milestones to ensure that they could graduate on schedule.
Course code |
Course name |
By Term / Year |
|---|---|---|
| MATH 1014 | Calculus II | Fall / Year 2 |
| PHYS 1114 | General Phys II | Fall / Year 2 |
| COMP 1022P | Introduction to Computing with Java | Spring / Year 2 |
| COMP 2011 | Programming with C++ | Fall / Year 3 |
| ELEC 1100 | Intro to Electro-Robot Design | Spring / Year 2 |
| ELEC 1200 | A System View of Communications: from Signals to Packets | Fall / Year 3 |
|
MATH 2011 / 2111 / 2350 / 2351 AND ELEC 2600 / 2600H |
Intro to Multivariable Calculus / Matrix Algebra and Applications / Intro to Differential Equations / Applied Linear Algebra and Differential Equations/ Probability and Random Processes in Engineering/ Honors Probability and Random Processes in Engineering | At least ONE by Fall / Year 3; and THREE by Spring / Year 3 |
| ELEC 2100 / 2100H / 2350 / 2400 | Signals and Systems / Honors Signals and Systems/ Computer Organization / Electronic Circuits | ALL by Spring / Year 3 |
| ELEC3XXX / 4XXX | TWO by Fall / Year 4 |
University Core and Required Courses
Introductory courses show students the big picture of ECE through two lab-based courses that all students must take early in their studies. Foundation courses provide students the core knowledge of ECE through four courses that all students must take as prerequisites for higher-level courses. Science / Math courses provide essential background knowledge to prepare students for higher-level courses. All students are required to take two Science courses, two Calculus courses, and three out of four other Math courses.
- School-Sponsored Courses (3 credits each from S&T SSC, SA SSC and H SSC) [9 Credits | 3 Courses]
- Science & Technology (S&T) [3 Credits | 1 Course]
- Social Analysis (SA) [3 Credits | 1 Course]
- Humanities (H) [3 Credits | 1 Course]
- Quantitative Reasoning (QR) [3 Credits | 1 Course]
- English Communication (in addition to the 6 credits of Comm. for Engineers) [6 Credits | 2 Courses]
- Chinese Communication [3 Credits | 1 Course]
- Healthy Lifestyle [0 Credit]
- Core Electives (S&T / SA / H / QR / Arts) [6 Credits | 2 Courses]
Total: 36 Credits | 12 Courses
Introductory Courses
- ELEC 1100 Intro to Electro-Robot Design (4 Credits)
- ELEC 1200 A System View of Communications: from Signals to Packets (4 Credits)
Foundation Courses
- ELEC 2100 Signals and Systems (4 Credits) OR ELEC 2100H Honors Signals and Systems (4 Credits)
- ELEC 2350 Introduction to Computer Organization and Design (4 Credits)
- ELEC 2400 Electronic Circuits (4 Credits)
Science Courses
- PHYS 1112 Honors General Phys I (3 Credits) OR PHYS 1312 General Phys I (3 Credits)
- PHYS 1114 General Phys II (3 Credits) OR PHYS 1154 Accelerated General Phys II (2 Credits) OR PHYS 1314 Honors General Phys II (3 Credits)
Math Courses
- MATH 1012 Calculus IA (3 Credits) OR MATH 1013 Calculus IB (3 Credits) OR MATH 1023 Honors Calculus I (3 Credits)
- MATH 1014 Calculus II (3 Credits) OR MATH 1024 Honors Calculus II (3 Credits)
- MATH 1020 Accelerated Calculus (4 Credits)
- MATH 2011 Intro to Multivariable Calculus (3 Credits)
- MATH 2111 Matrix Algebra and Applications (3 Credits)
- MATH 2350 Applied Linear Algebra and Differential Equations (3 Credits)
- MATH 2351 Intro to Differential Equations (3 Credits)
- ELEC 2600 Probability and Random Processes in Engineering (4 Credits) OR ELEC 2600H Honors Probability and Random Processes in Engineering (4 Credits)
Comp Courses
- COMP 1022P Introduction to Computing with Java (3 Credits)
- COMP 2011 Programming with C++ (4 Credits)
Senior Courses
Senior courses broaden students' horizon and equip them with the necessary tools in different ECE areas, and allow students to deepen their knowledge within a selected area of interest. Students are required to take at least 21 credits of senior courses including at least two ELEC 4000-level courses.
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3180 | Data-Driven Portfolio Optimization | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 3210 | Machine Learning and Information Processing for Robotics | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 3810 | Data Science in Neural Engineering | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4130 | Machine Learning on Images | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4240 | Deep Learning in Computer Vision | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 3100 | Signal Processing and Communications | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4840 (former 4010N) | Artificial Intelligence for Medical Image Analysis | Spring |
* Subject to change
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3810 | Data Science in Neural Engineering | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4810 | Introduction to Biosensors and Bioinstrumentation | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4820 | Medical Imaging | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4840 (former 4010N) | Artificial Intelligence for Medical Image Analysis | Spring |
* Subject to change
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3200 | System Modeling, Analysis and Control | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 3210 | Introduction to Mobile Robotics | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4210 | Control System Design | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4220 | Introduction to Robotics | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4240 | Deep Learning in Computer Vision | Spring |
* Subject to change
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3600 | Electromagnetics: from wireless to photonic applications | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4610 | Engineering Optics | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4620 | Photonics and Optical Communications | Fall |
* Subject to change
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3300 | Introduction to Embedded Systems | Fall/Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 3310 | Digital Fundamentals and System Design | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4320 | FPGA-based Design: From Theory to Practice | Fall |
* Subject to change
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3400 | Introduction to Integrated Circuits and Systems | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4410 | CMOS VLSI Design | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4420 | Analogue Integrated Circuits Design and Analysis | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4430 | Integrated Power Electronics | Spring |
* Subject to change
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3500 | Integrated Circuit Devices | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4510 | Semiconductor Materials and Devices | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4520 | Integrated Circuit Fabrication Technology | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4530 | Fundamentals of Photovoltaic and Renewable Energy | Spring |
* Subject to change
Level |
Course Code |
Course Title |
Offering Term* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senior | ELEC 3100 | Signal Processing and Communications | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 3120 | Computer Communication Networks | Fall and Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 3180 | Data-Driven Portfolio Optimization | Spring |
| Senior | ELEC 4110 | Digital Communications and Wireless Systems | Fall |
| Senior | ELEC 4130 | Machine Learning on Images | Fall |
* Subject to change
Recommended Study Patterns (To be provided)
The recommended study patterns help students plan their studies in selected areas.
Curriculum of Other Years of Entry
Students must adhere to the curriculum of the year of entry throughout their program of study. Details of the degree and major requirements can be found in the program catalog of the year of intake.
Final Year Projects/Theses
All ECE students are required to complete a Final Year Project/Thesis (FYP/T). It is an excellent opportunity for them to synthesize the theory and experimental work they learned during the Program in order to complete the project.
Industrial Experience
All ECE students are required to undertake practical training as a compulsory graduation requirement. Students could gain valuable hands-on experience through training and enhance their understanding and appreciation of the knowledge acquired in classrooms and laboratories. To satisfy the practical training requirement, students may either complete an internship or the required Industrial Training modules.
Minor Program
Undergraduate students may enroll in a minor program in addition to their disciplinary major if they meet the enrollment conditions specified. On successful completion of both major and minor programs, the student will receive a degree in their major subject with a minor in their selected program.
The Minor Program in Robotics aims at providing interested students with a comprehensive selection of courses on robotics, control, and automation, allowing students to form a study pattern tailored to fit his/her own interest and focus. The courses in this Minor Program cover basic C programming, embedded systems, mechatronics design, control systems design, aerial robotics, machine learning, etc. Students are also required to complete a project-based course. The program will provide both theoretical foundation and hand-on experience to the students, enabling them to acquire sufficient and necessary tools and skills to solve practical and fundamental problems.
Program Director: Prof. Ling SHI
The Sustainable Energy Engineering Minor is to provide the interested student with a comprehensive selection of courses on sustainable development and energy, thus allowing the student to formulate a study program catered to his/her own interest or emphasis. The courses in this Minor program will cover energy production, distribution, usage and storage, as well as the public policy context in which the flow of energy from production to consumption is regulated. Additionally, the program will help students understand both the environmental and economic impact of sustainable development, as well as the impact of policy and mandate on the promotion and adoption of sustainable energy.
Program Director: Prof. Yajing SHEN
Required Courses
- COMP 2011 Introduction to Object-oriented Programming (4 Credits)
- COMP 2012 Object-Oriented Programming and Data Structures (4 Credits)
Elective Courses
- 10 Credits of IT elective (~3 Courses)
- To be chosen from amongst any COMP courses (except COMP 1001). Students may also use up to 6 credits of non-COMP courses (~2 Courses) to count towards this requirement. Non-COMP courses include:
- ELEC 2300 Computer Organization
- ELEC 4120 / 3120 Computer Communication Networks
- ELEC 4130 Digital Image Processing
- ELEC 4170 / 3170 Digital Media and Multimedia Applications
- MATH 2343 Discrete Structures
Total credit requirement: 18 Credits
Recommended Study Pattern
Year / Term |
Course |
Total # of Credits* |
|---|---|---|
| Year 1 / Fall |
|
9 Credits |
| Year 1 / Spring |
|
12-13 Credits |
| Year 2 / Fall |
|
13 Credits |
| Year 2 / Spring |
|
15 Credits |
| Year 3 / Fall |
|
16 Credits |
| Year 3 / Spring |
|
11-12 Credits |
| Year 4 / Fall |
|
15-17 Credits |
| Year 4 / Spring |
|
9-10 Credits |
*120 credits in approved courses to graduate
Double Major
With the approval of the major department, undergraduate students can graduate with dual program designation (e.g. BEng in Electronic Engineering AND Computer Engineering), if they can complete the requirements of the two undergraduate programs within the normal period of study.
Exchange Programs
The University has established exchange programs with leading institutions, such as UC Berkeley, University of Michigan, UCLA, University of Pennsylvania, Tsinghua University, University of Science and Technology in China, and is in active negotiation with a number of institutions. These exchange programs intend to provide opportunities for students to study abroad and enhance their international exposure and future career development.
Academic Advising
The ECE Department has set up several channels to help students in academic affairs: student advising courses and FYP supervisors. All students have a mentor for each year of their major study, and they should make use of these chances to ask questions and discuss academic issues (comment on courses, instructors, career planning, further study, etc.).
Professional Recognition
Our programs are recognized by the Hong Kong Institution of Engineers (HKIE). Graduates from our programs with honors will be deemed to have satisfied the educational requirement for Corporate Membership of HKIE.
Career Prospects
A wide variety of career paths are available to MEIC graduates. Upon graduation, we expect our graduates to take positions in the industry as electronic engineers, communication engineers, system analysts and designers, information technologists, computer project managers and many other technical and managerial positions. A significant portion chooses to continue their study at the postgraduate level. Even graduates who choose not to pursue technical careers find that the engineering training they obtained at HKUST has given them a competitive advantage over their co-workers.
The list of employers includes many world-class local and overseas companies, such as ASM, ASTRI, HKT, Huawei, Lenovo, Microsoft, National Semiconductor, Philips, Smartone, Solomon Systech, Varitronix, etc.
Enquiries
Email: eequestions@ust.hk